Graph Layouts
The different layout styles are responsible for determining the locations of all diagram elements based on different optimization criteria. A variety of layout styles are included: Hierarchic, organic (force-directed), tree, orthogonal, circular, radial and series-parallel. All layout algorithms can be applied to a diagram in an animated fashion. Almost all aspects of each layout algorithm can be changed to fit to a specific domain and use case.
Evaluation
Try yFiles for freeBrowse our
extensive graph-layouts!

Hierarchic

Organic

Tree

Orthogonal

Circular

Radial

Series-parallel

Radial tree
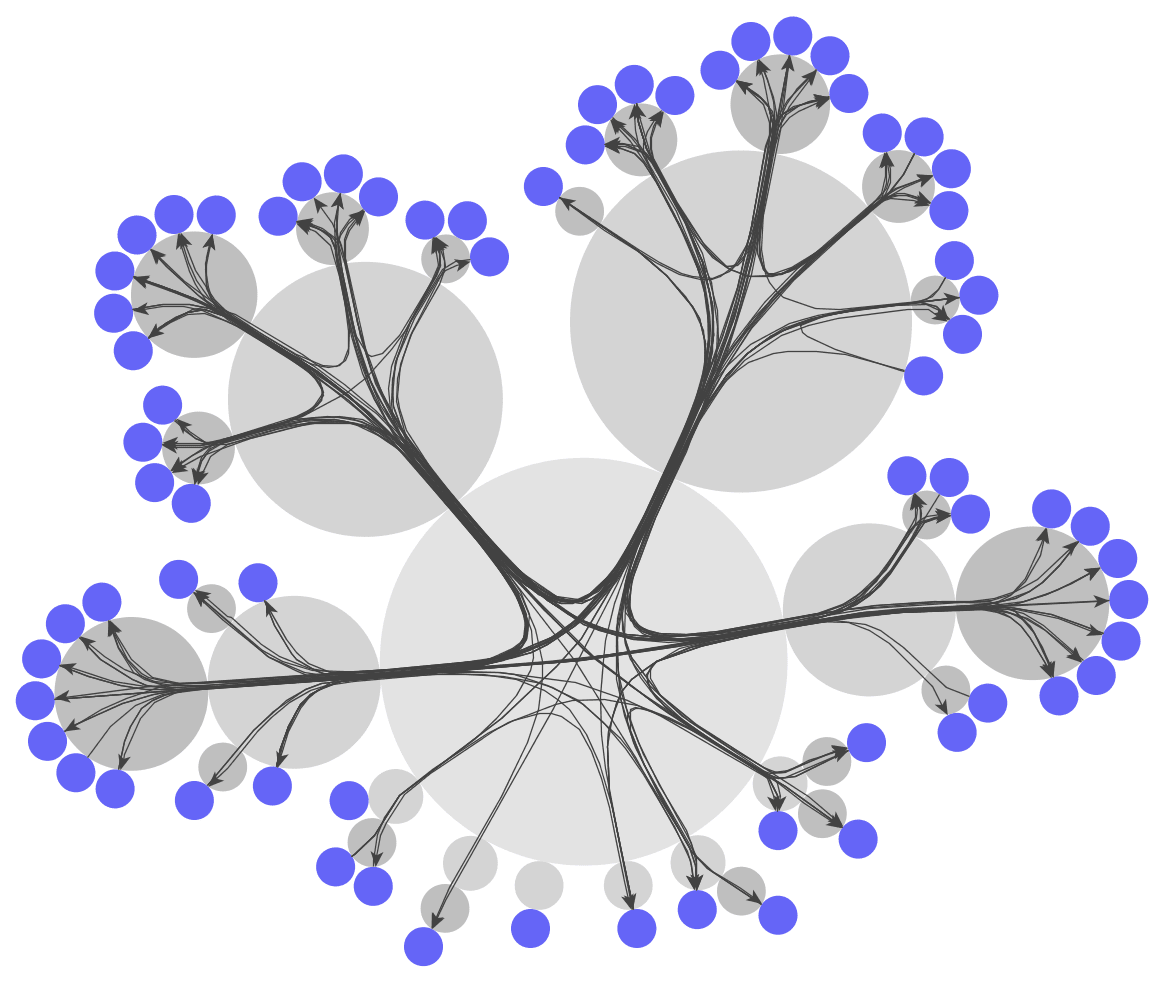
Radial groups

Compact Disk

Tabular
Select a layout above...
Properties of visualization
- nodes are distributed over layers
- different edge routing styles
- sub-components
Typical use cases
- flow charts, decision diagrams
- process modelling, UML and activity diagrams
- call graphs (software development)
Properties of Graph
- directed edge play important role
Properties of visualization
- natural distribution of nodes, symmetric properties
- nodes are placed close to their neighbors
- edges are straight-line
Typical use cases
- large networks
- social network analysis
- emphasis of structures, e.g., trees, cycles, stars
Properties of Graph
- no limitations
Properties of visualization
- parent-child relationship is emphasized
Typical use cases
- network management
- Business administration, e.g., organization charts
- parent-child-relations
Properties of Graph
- graph is a tree (and may have a dedicated root node)
- with tree reduction stage support of graphs that are not trees
Now that you’re here,
you might want to explore
you might want to explore
Why, how, what? —Just ask the diagramming experts!

Our team is happy to advise you – no strings attached. Let's talk about your project and find the perfect solution for your needs!
E-mail: hello@yworks.com
Thank you!
Your message has been sent.
Your message has been sent.
We are sorry,
Your request could not be sent. Please reload the page and try again.
If the problem persists, please report the error to webmaster@yworks.com.
Your request could not be sent. Please reload the page and try again.
If the problem persists, please report the error to webmaster@yworks.com.
The data you enter will only be used to contact you regarding your request.
Learn more in our privacy policy.
Learn more in our privacy policy.




